Deploying a static site on AWS
A tutorial of how to deploy a static site from an AWS S3 bucket.
Overview
In this tutorial I will show you how to deploy a static site on AWS via an S3 bucket.
Related Tutorials
- Creating a static website using Jekyll (coming soon).
- Deploying a static site on AWS (this tutorial).
- Serving Static Site from S3 Bucket over HTTPS with Cloudfront (coming soon).
- Automating the deployment of a static site using Github Actions (coming soon).
Prerequisites.
- AWS Account.
- Domain in Route53 *This is optional. Only needed if you want to serve the site from a custom domain.
- A static site.
Tutorial
1. Creating the S3 Bucket.
Go to S3 in the AWS Console and create a new bucket.
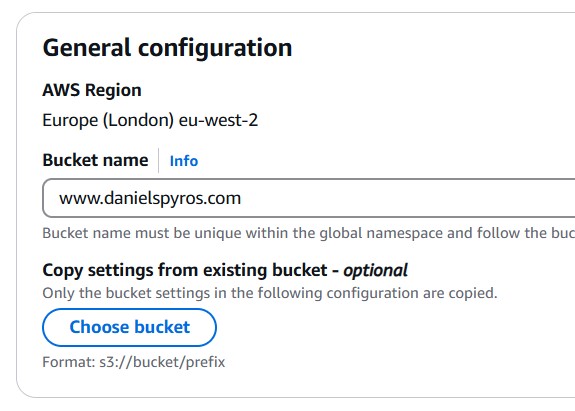
Give the S3 bucket a name. I recommend giving the bucket the same name as the URL from which you would like to serve the site. This is not mandatory if you complete part 2 of this tutorial to use a cloudfront distribution.
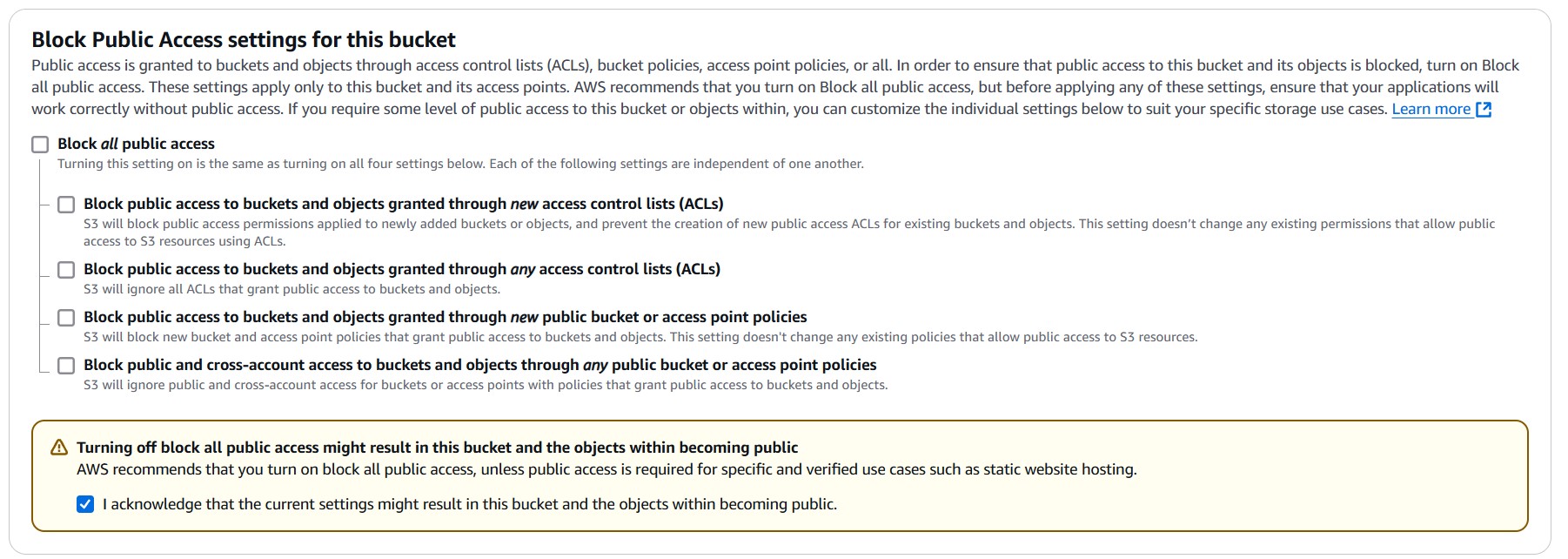
Uncheck “Block all public access” and check the acknowledgement. We will need this to be able to serve the site from the S3 bucket. Again I believe it is not needed when connected to the cloudfront distribution.
2. Uploading the site to the S3 Bucket.
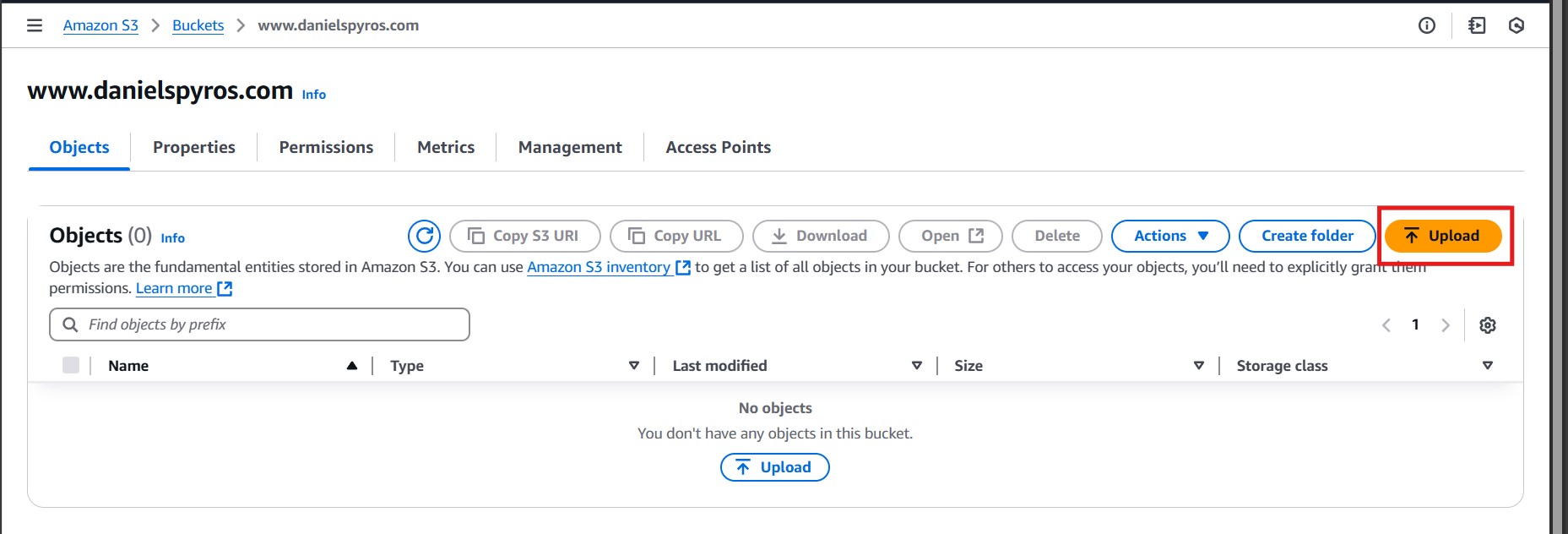
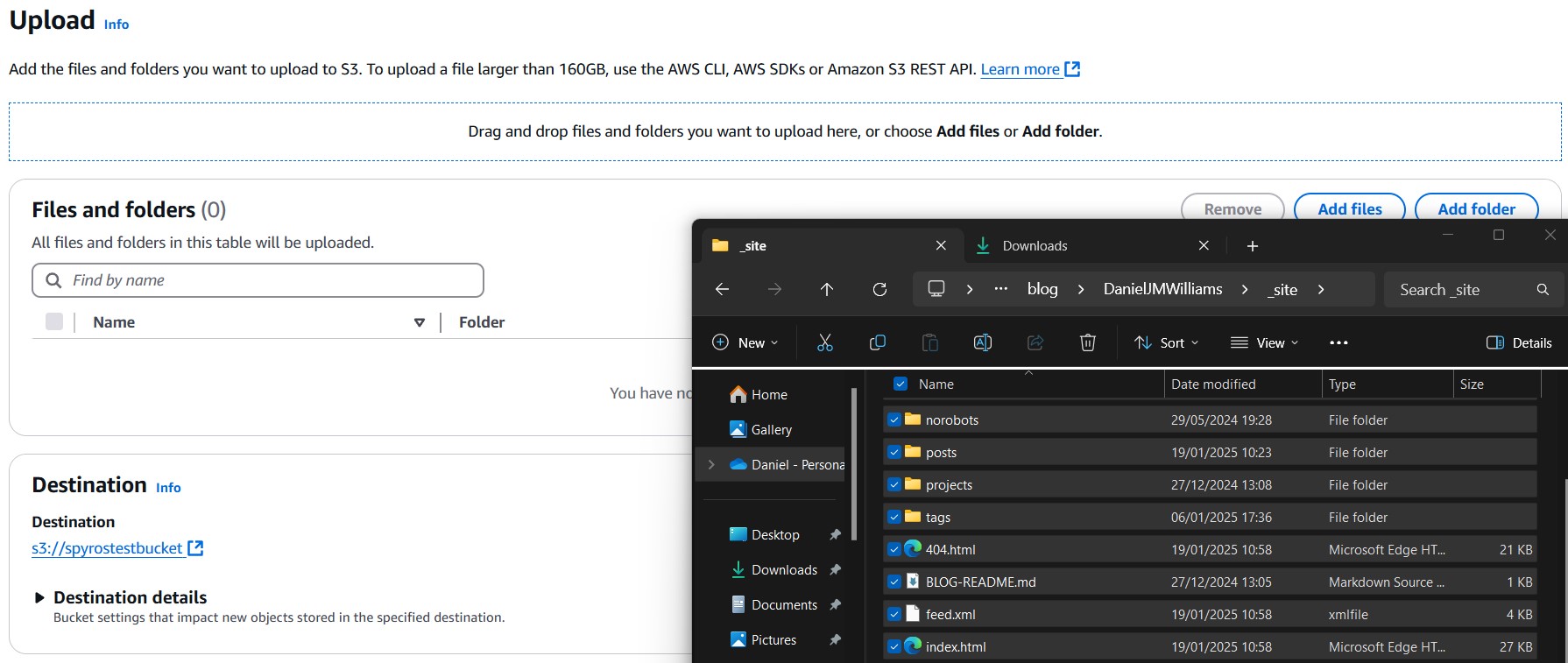
Upload your site’s HTML and assets to the S3 bucket. In my case, I am using Jekyll so I need to make sure Jekyll has compiled the project by running jekyll serve and then uploading the contents of the _site directory.
Make sure that index.html end up in the root directory of the bucket instead of a subfolder. I recommend dragging and dropping the files or using the AWS CLI to do this. Using the “Add Folder” button put my files in a _site subfolder so I had to remove and readd them.
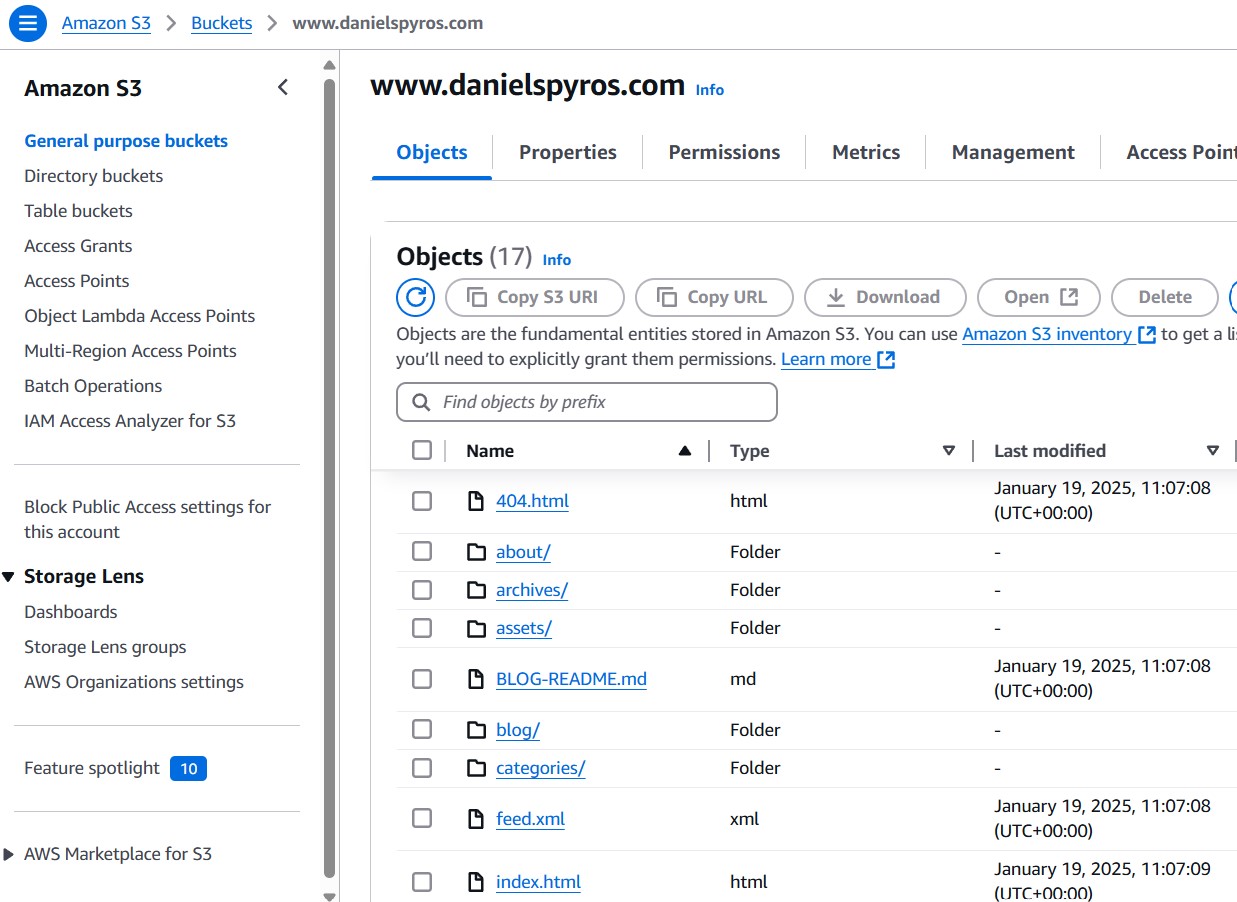
Once uploaded, it should look something like this:
In a later tutorial, I will show you how to automatically upload to the S3 bucket when we push new changes to the Github repository using Github Actions.
3. Configuring the S3 Bucket for Static Website Hosting.
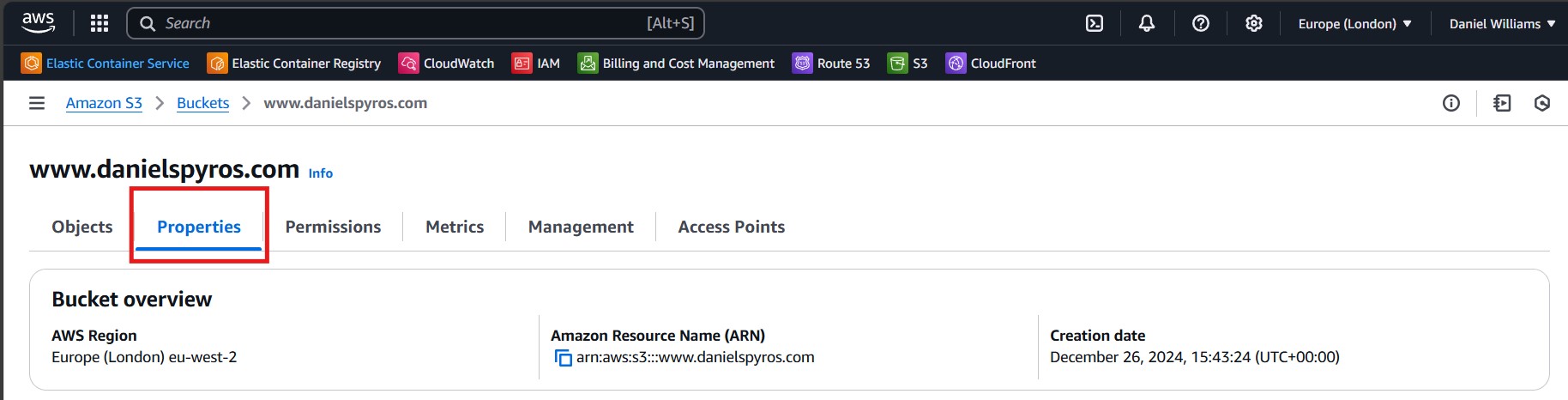
Now go to the properties tab of your S3 bucket.
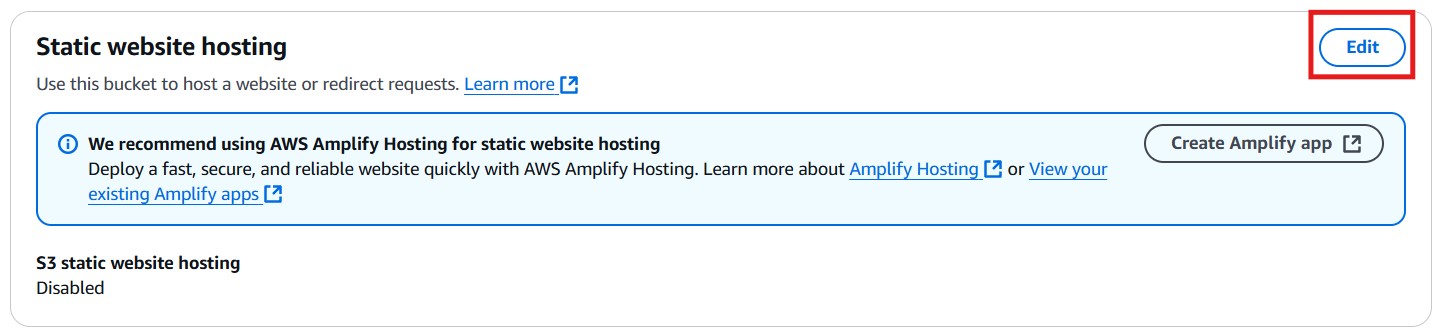
Scroll to the bottom where it shows “Static website hosting” and click “Edit”.
Enable static website hosting. Leave the hosting type as “Host static website”, and set the index and error documents as necessary.
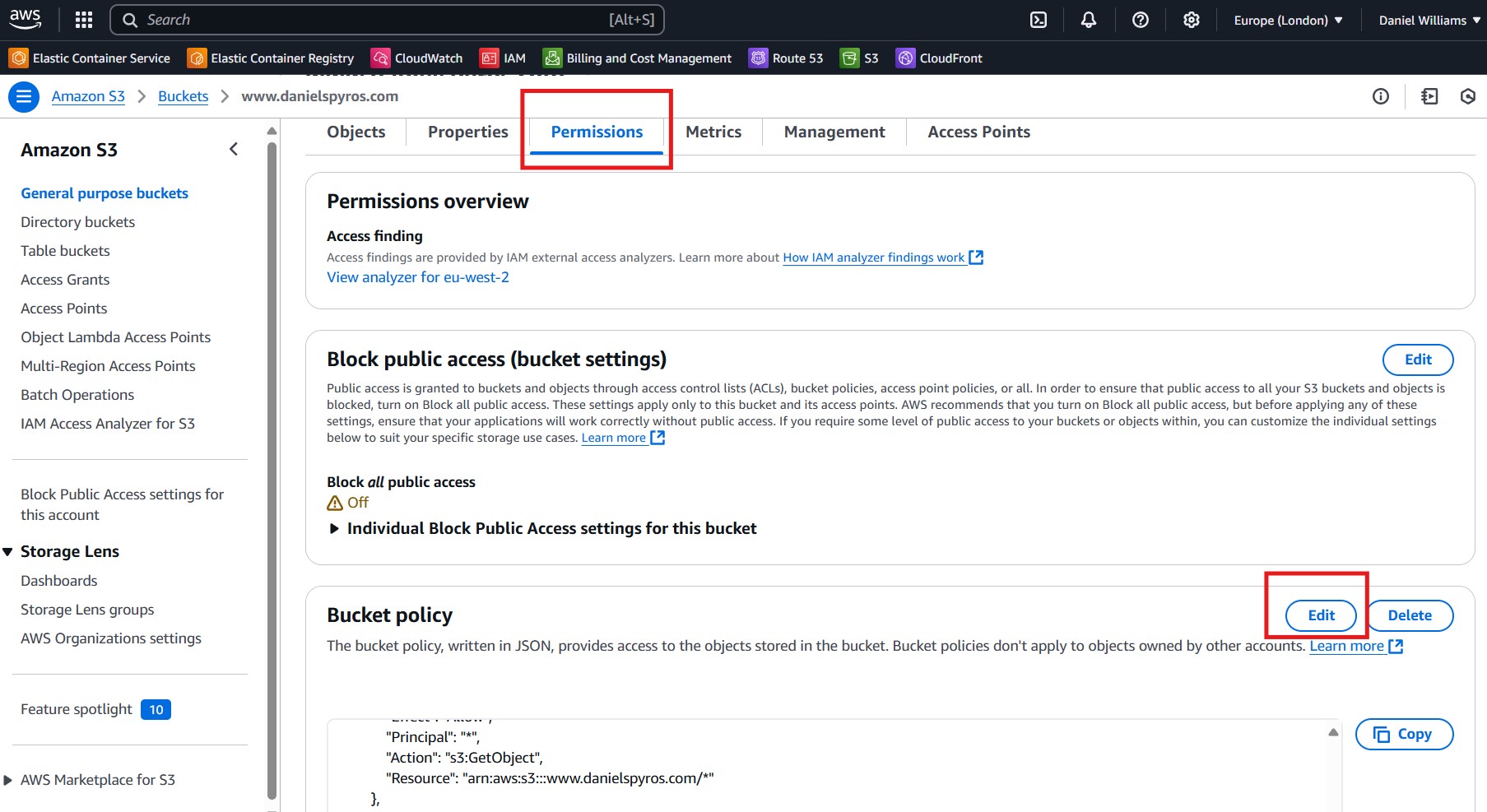
4. Setting the Bucket Permissions.
Now go to the Permissions tab and edit the bucket policy.
Paste in this JSON policy:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
{
"Version": "2008-10-17",
"Id": "DanielSpyrosBucketPolicy",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "AllowPublicReadAccess",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": "*",
"Action": "s3:GetObject",
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::www.danielspyros.com/*"
}
]
}
Update the bucket name from www.danielspyros.com to the name of your bucket. Also update the Id of the policy - this can be whatever you want, or you can remove it.
Now save the policy.
TODO: check if this policy is necessary at this step.
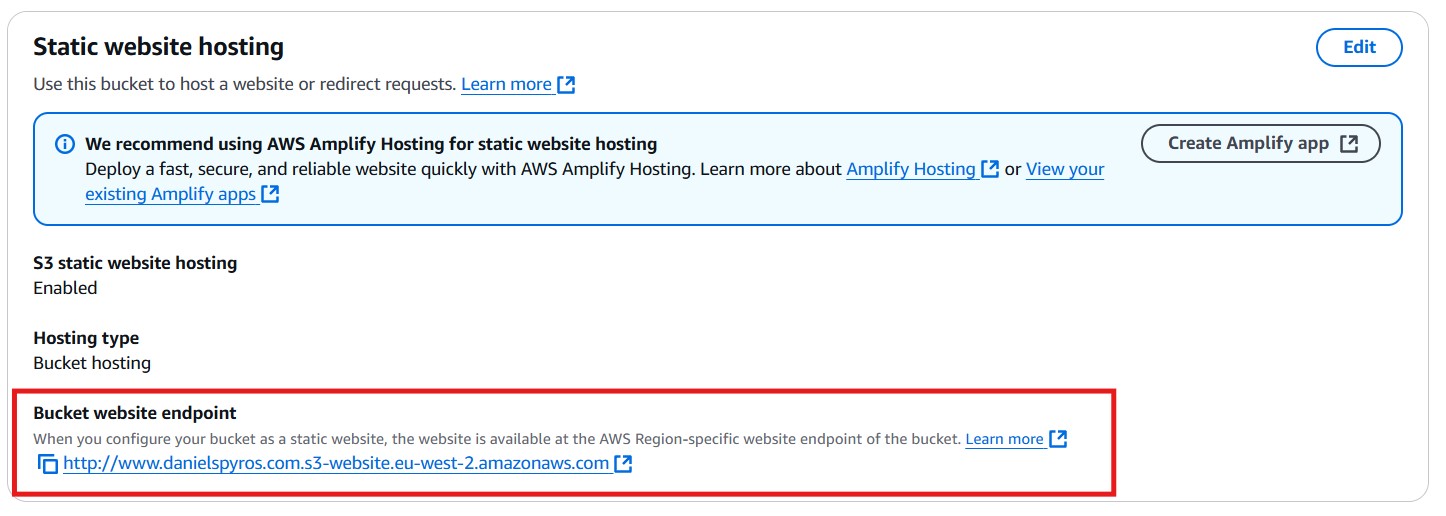
5. Viewing the site from the S3 Bucket URL.
Go to the Properties tab again, scroll to the bottom and find the URL where your bucket is being hosted.
Click the link and view your site.
6. Linking to a custom domain.
7. Viewing the site from your custom domain.
Voilà.
In the next tutorial, I will show you how to serve the site over HTTPS with a cloudfront distribution. After that, I will show you how to automatically update the site with Github Actions CICD.